Since November 2019, two papers of the Research Group led by Professor Shang Xuequn have been accepted by Bioinformatics, a top journal of Biological Information. Founded in 1998, Bioinformatics is the top journal for the latest and most advanced research progress in the field of Biological Information. Under the operating of Oxford University Press, it is an official journal of the International Society for Computational Biology (ISCB), belonging to the Tier 1 journal in CAS Journal Ranking system.
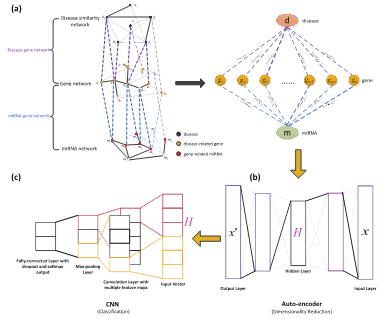
Entitled A learning-based frame work for miRNA-disease association identification using neural networks, the first paper develops the world's first in-depth learning model for predicting disease-related microRNA (miRNA), a kind of non-coding RNA. Numerous studies have shown that miRNA is closely related to a variety of diseases, so it is a potential drug target for many diseases. In this paper, a three-layer network model containing richer miRNA and disease-related information is constructed, which can predict the relationship between miRNA and diseases by obtaining miRNA and disease characteristics through in-depth learning model. Associate Professor Peng Jiajie, Associate Professor Chen Bolin, the young teachers of the Research Group and postgraduate students Hui Weiwei and Li Qianqian are the co-authors of the paper. Professor Shang Xuequn is the correspondence author.
Another paper, entitled Identifying emerging phenomenon in long temporal phenotyping experiments, proposes a method to identify temporal patterns of phenotypic variation from high-throughput temporal phenotypic data. Temporal patterns of phenotypic variation refer to different genotype samples that show consistent phenotypic variation trend in a relatively short continuous time. In this paper, dynamic network model is used to describe high-throughput time series phenotypic data, and then temporal patterns of phenotypic variation are identified. In addition, directed acyclic network is used to describe the relationship between different temporal patterns of phenotypic variation. This algorithm can not only analyze the temporal phenotypic data but also be widely used in the analysis of various high-throughput temporal data. This paper was completed in collaboration with Professor David Kramer of Michigan State University and Professor Jin Chen of the University of Kentucky. Peng Jiajie, a young Associate Professor of the Research Group, and Lu Junya, a postgraduate student, are the co-authors of the paper, while Professor Shang Xuequn is the correspondence author.
The Research Group guided by Shang Xuequn belongs to the Key Laboratory of Big Data Storage and Management under Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, which is under the charge of Professor Li Zhanhuai. Under the leadership of Professor Shang Xuequn, the Research Group has gained a series of research results in the emerging interdisciplinary field of computer science and biomedicine in recent years, and has undertaken 2 key projects and more than 10 general and youth projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China. In 2019 alone, it published over 30 papers in authoritative journals or conferences such as Bioinformatics, Nucleic Acid Research, BMC Bioinformatics, BIBM, AAAI and CIKM, of which more than 20 were published in Tier 1 and Tier 2 journals in CAS Journal Ranking system. By fully employing the advantages of all teachers with overseas study experience in famous universities, the team has actively cooperated with internationally renowned universities such as Harvard University, Yale University, The University of Michigan, University of Toronto, Emory University, University of Alberta and National University of Singapore, and will send doctoral students and master students to the above universities for exchange and study every year. Next, the Research Group will continue to carry out in-depth big data processing and analysis and further promote the application of research results by centering on our country's major strategic needs.
Writer: Peng Jiajie
Reviewer: Gao Wu